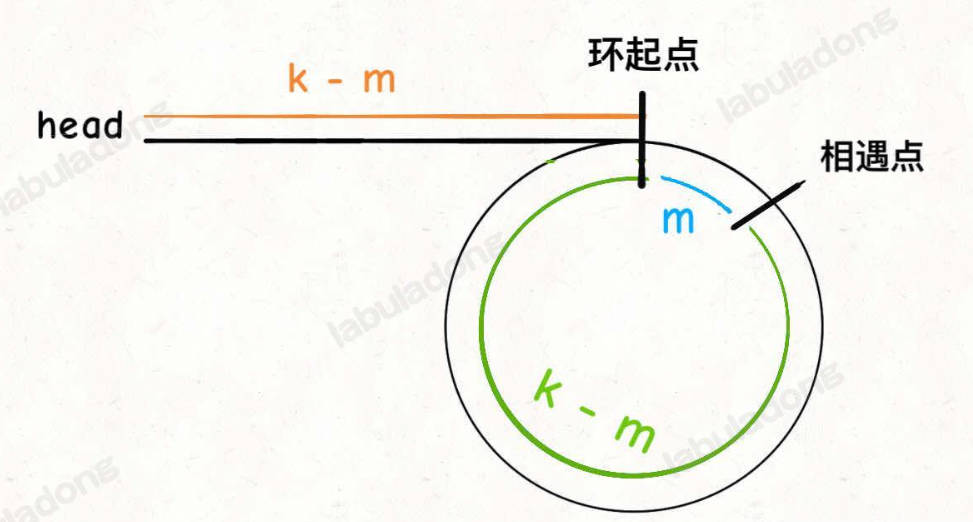
142. 环形链表 II
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast,slow;
fast = slow = head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(slow == fast) break;
}
if(fast == null || fast.next == null) return null;
slow = head;
while(fast!=slow){
fast=fast.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
|

21. 合并两个有序链表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode head= new ListNode(0),cur = head;
while(list1!=null && list2!=null){
if(list1.val<=list2.val){
cur.next=list1;
list1 = list1.next;
}
else{
cur.next=list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = list1!=null?list1:list2;
return head.next;
}
}
|
什么时候需要用虚拟头结点?我这里总结下:当你需要创造一条新链表的时候,可以使用虚拟头结点简化边界情况的处理。
比如说,让你把两条有序链表合并成一条新的有序链表,是不是要创造一条新链表?再比你想把一条链表分解成两条链表,是不是也在创造新链表?这些情况都可以使用虚拟头结点简化边界情况的处理。
86. 分隔链表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
ListNode p = head;
ListNode head1=new ListNode(-1),cur1 = head1;
ListNode head2=new ListNode(-1),cur2 = head2;
while(p!=null){
if(p.val>=x){
cur2.next = p;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
else{
cur1.next = p;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
ListNode temp = p.next;
p.next = null;
p=temp;
}
cur1.next = head2.next;
return head1.next;
}
}
|
注意:断开原list 如果不断开原链表中的每个节点的 next 指针,那么就会出错,因为结果链表中会包含一个环。
总的来说,如果需要把原链表的节点接到新链表上,而不是 new 新节点来组成新链表的话,那么断开节点和原链表之间的链接可能是必要的
23. 合并K个升序链表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if(lists.length==0) return null;
PriorityQueue<ListNode> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(lists.length,(a,b)->(a.val-b.val));
ListNode dump = new ListNode(-1),p=dump;
for(ListNode head:lists){
if(head!=null){
pq.add(head);
}
}
while(!pq.isEmpty()){
ListNode temp = pq.poll();
p.next = temp;
if(temp.next!=null) pq.add(temp.next);
p=p.next;
}
return dump.next;
}
}
|
19. 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
fast=fast.next;
}
if(fast==null) return head.next;
while(fast.next!=null){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slow.next=slow.next.next;
return head;
}
}
|
考虑头结点 若删的是头结点 则null.next报错
876. 链表的中间结点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode p = head;
ListNode q = head;
double count=0;
while(p.next!=null){
count++;
p=p.next;
}
count = Math.ceil(count/2);
while(count>0){
q=q.next;
count--;
}
return q;
}
}
|
160. 相交链表
⭐
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode p1 = headA;
ListNode p2 = headB;
while(p1!=p2){
if(p1==null) p1=headB;
else p1=p1.next;
if(p2==null) p2=headA;
else p2=p2.next;
}
return p1;
}
}
|